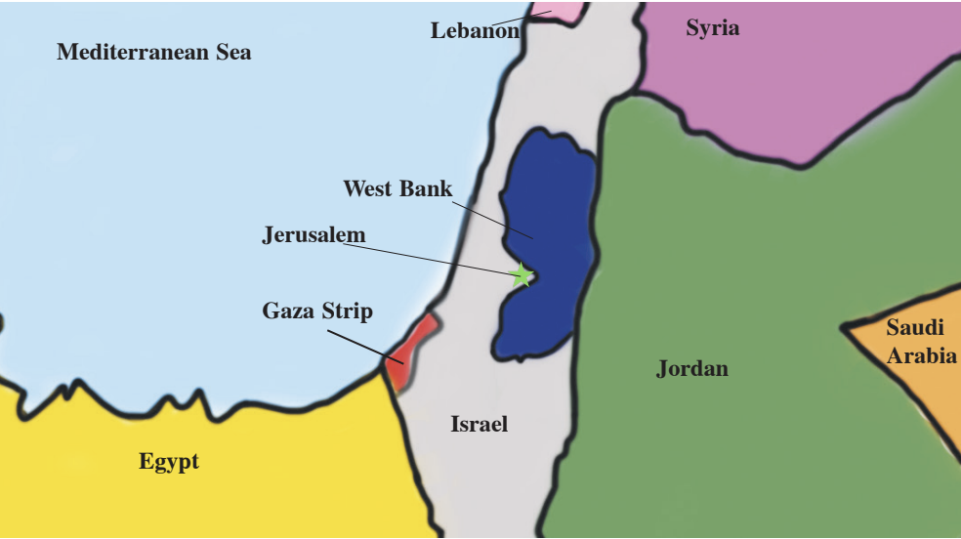
The Spectrum recognizes that this conflict is very complicated, and often, both sides claim that it was started by the other. Spectrum has decided that we will start this timeline when Western nations first get involved. Furthermore, the timeline printed on this page is not comprehensive.
November 2, 1917: The Balfour Declaration is signed
Arthur James Balfour, the British Foreign Secretary, wrote a letter supporting “the establishment in Palestine of a national home for the Jewish people.” Response to the declaration did not include the perspective of the Palestinian people.
August 24, 1929: Hebron Massacre
In the city of Hebron, approximately 70 Jews were murdered by Arabs. This led to the end of Jewish presence in Hebron until after the Six-Day War.
May 23, 1939: The White Paper of 1939 is ratified
The White Paper limited Jewish immigration and occupation in Palestine and was written in response to the Arab Revolt, a three-year-long protest by Arabs over Jewish immigration and British occupation.
November 29, 1947: United Nations Resolution 181 is passed
Created in response to the Holocaust, this resolution called for dividing Palestine into separate Arab and Jewish states while Jerusalem would remain the property of no one. The proposal was approved by Jewish leaders but rejected by Arab states and Palestinian citizens.
May 14, 1948: Independence Day War
After Israel declared its independence from the British Mandate and established the State of Israel, Egypt, Jordan, Syria, Iraq, and Lebanon invaded Israel, resulting in 6,000 Israeli deaths and 10,000 Arab deaths. After the war, an armistice agreement gave Israel more territory than it had under Resolution 181, displacing over 700,000 Palestinians in an event commonly known as Nakba (catastrophe).
October 29-November 7, 1956: Sinai War
Israel, along with the United Kingdom and France, invaded Egypt after the nationalization of the Suez Canal, meaning that Egypt would then control the revenue from the Suez Canal. Over 1500 people were killed, including 1000 civilians.
May 28, 1964: The Palestine Liberation Organization is Founded
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO), is formed with the goal of replacing Israel with an Arab State.
June 5-10,1967: The Six-Day War
After an increase in attacks against Israel and an alliance forming between Jordan, Egypt, and Syria, Israel preemptively attacked all three of these countries. The war resulted in Israel claiming the Golan Heights, Sinai Peninsula, Gaza Strip, West Bank, and East Jerusalem.
September 5, 1972: Munich Massacre
At the 1972 Munich Olympics, 11 members of the Israeli Olympic team were killed during an attempted hostage trade by Black September, a Palestinian group. Black September’s demands were the release of over 230 hostages in Israel and Germany. All the members of Black September involved in the attack were killed during a shootout with the police, along with one German police officer.
October 6-25, 1973: Yom Kippur War
After growing tensions stemming from Israel’s unwillingness to return the territory it had claimed during the Six-Day War, Egypt, and Syria invaded Israel simultaneously on different parts of Israel’s border. 8,000-15,000 people were killed in total.
September 17, 1978: Camp David Accords are Signed
Following 12 days of negotiations under Jimmy Carter at Camp David, Egypt, and Israel came to the first peace treaty between Israel and an Arab nation. As a result of the Accords, Israel left the Sinai Peninsula and Egypt formally recognized Israel as a nation.
1982-1985: First Lebanon War
Following the PLO’s increased presence in Lebanon and the attempted assassination of the Israeli Ambassador in London, Israel attacked the PLO in Lebanon. After the PLO responded with rockets, Israel sent ground troops into Lebanon. In 1985, a security zone was formed. Due to the killing of Israeli troops by Iranian and Syrian terrorist groups, Israel withdrew from the security zone in 2000.
December 8, 1987-September 13, 1993: First Intifada
The First Intifada —Palestinian uprising— took place in Israel and the Israel-occupied Palestinian territories. The uprising featured both violent and non-violent aspects, including graffiti, Molotov cocktails, and economic boycotts. Near the end of the Intifada, the newly elected Israeli government and the PLO started secret negotiations for peace.
1987: Founding of Hamas
During the First Intifada, Hamas, a terror organization, was founded. The group’s original charter calls for replacing Israel with an Islamic-Palestinian state.
1993-1995: Oslo Accords
The Oslo Accords were an attempt at peace between Yitzchak Rabin’s Israeli government and the PLO (negotiated by the Clinton administration). Due to the rise of Hamas, and the attacks that they committed on Israel, the Accords fell apart.
October 26, 1994: Israel-Jordan Peace Treaty
Israel and Jordan signed a peace treaty that ended their state of war and established full diplomatic relations between the countries, including setting a clear border.
November 4, 1995: Assasination of Yitzchak Rabin
While Prime Minister Rabin was attending a rally in support of the Oslo Accords, a supernationalist Israeli assassinated him at the rally.
September 28, 2000-February 8, 2005: Second Intifada
The violence started during Prime Minister Ariel Sharon’s visit to the Al-Aqsa Mosque, with Palestinian riots being responded to with force by the Israeli police. The uprising caused over 3,400 fatalities and led to the construction of the West Bank barrier, similar to the one built in Gaza in 1996.
September 12, 2005: Israel Evacuation from Gaza is Completed
Following the Intifada, Israel evacuated from Gaza, both militarily and residentially. With some pressure from the United States, Israel also evacuated four small settlements in the West Bank. The full “disengagement” is disputed because Israel still controls Gaza’s airspace and territorial waters.
July 12-August 14, 2006: Second Lebanon War
Due to the murder of eight Israeli soldiers and two hostages taken, Israel attacked homes associated with Hezbollah, a Lebanese political party and militant group. In response, Hezbollah rapidly increased the number of rockets launched into Israel. The war resulted in more than 1100 deaths.
2006-2007: Rise of Hamas in Gaza
Following its victory in the 2006 elections, Hamas initiated a military takeover of Gaza, but Fatah (the former Palestinian leader) still controls the West Bank. As of Dec. 2023, this was the final Palestinian election.
December 27, 2008-January 18, 2009: First Gaza War
In response to Hamas’ attacks on Sedot, an Israeli city, Israel launched a 22-day ground invasion in Gaza. Over 1000 Palestinians were killed before a ceasefire.
July 8-August 26, 2014: Second Gaza War
After the kidnapping and killing of three Israeli teens led to an aerial conflict between Israel and Hamas, Israel launched a limited ground invasion into Gaza to destroy tunnels built by Hamas that led into Israel.
September 15, 2020, December 22, 2020, and January 6, 2021: Abraham Accords are Signed
Following mediation by the United States, Israel signed peace treaties and normalized diplomatic relations with Bahrain, the United Arab Emirates, Morocco, and Sudan. This marked the first time since 1994 that Israel normalized relations with an Arab nation.
May 10-21, 2021: Conflict in Gaza
Following hostilities between Palestinians and Israeli police officers at the Al Aqsa Mosque, Hamas launched rockets at Israeli civilians. A ceasefire was brokered by Egypt, Qatar, and the United Nations.
August 2022: Israel-Jihad Conflict
Due to the imminent threat of an invasion by the Islamic Jihad, Israel attacked Iranian military bases. The Jihad responded by sending over 1000 rockets into Israel.
October 7, 2023: Hamas Massacre
Hamas launched a surprise attack on several Israeli communities, causing over 1200 Israeli deaths.
October-December 2023: Israel-Hamas War
Israel has fired over 10,000 rockets into Gaza, and Hamas has fired over 10,000 rockets into Israel. Over 15,000 Palestinians and 1,000 Israelis have been killed.
November 24-30, 2023: Ceasefire
Following the Oct. 7 Hamas attack on Israel communities, there was a four-day four ceasefire to relieve hostages taken during the attack.
SOURCES:
Timeline of conflict between Israel and Palestinians in Gaza | Reuters
Israel-Hamas war updates: Houthi vessel seizure in Red Sea ups the stakes | Al Jazeera
Timeline: Key Events In The Israel-Arab And Israeli-Palestinian Conflict | AJC
Israel-Hamas war: Cease-fire extended for two more days | AP News
What are the roots of the Israel-Palestine conflict? | Israel-Hamas war | The Guardian
What happened when Israel invaded Gaza in 2014? – CBS News
Brittanica (multiple articles)
Milestones in the History of U.S. Foreign Relations
Israeli Embassy